
by Rodric David, founder/CEO, Thunder
History records epochs that impact human behavior and culture in ways that were previously unimaginable. The Industrial Revolution, in a relatively short period of time, materially impacted the lives of all people, industries, businesses, and governments through the invention and commercialization of new technologies.
These innovations impacted trade, products, society, art, and culture. The exploitation of many new technologies, inventions, and processes empowered entrepreneurs to conceive of new and fantastic opportunities.
Austrian economist Joseph Schumpeter, studying the rapid changes that occurred during the Industrial Revolution, recognized that growth in a capitalist society happened through the introduction of innovations which create chaos and structural change in society. In 1942 he characterized the entrepreneur as the source of the “creative destruction” necessary for major economic advances.
The Internet
The Internet is the defining technology of the Information Age (the most recent transformative epoch) and its emergence in 1993-94 unleashed the greatest creative destruction process in human history. In fewer than 25 years, the Internet has impacted the lives of every human on the planet, created unprecedented wealth, raised millions out of poverty, and changed every industry and business globally.
The emergence of the Metaverse over the next ten years will exceed the creative destruction brought about by the Internet and will empower the Creator Economy.
“Situations emerge in the process of creative destruction in which many firms may have to perish that nevertheless would be able to live on vigorously and usefully if they could weather a particular storm.”
Joseph Schumpeter
When I graduated from the University of Southern California in 1993, I could never have imagined how pervasive and important to my life the Internet (formerly the World Wide Web) would become.
Access to the Internet is now considered by governments and citizens as an essential right with the same importance as access to clean water. Most of us spend multiple hours every day interacting with the Internet for work, shopping, banking, entertainment, social media and more. It is with a sense of déjà vu that I sit here writing this article about the Metaverse and its pending impact on all our lives, as if 2021 is 1993 all over again.
The Internet was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 and entered the public domain in 1993-94 when websites for general use became accessible. By the end of 1993, there were 623 websites on the internet. By mid-1994 there were 2,738 websites, according to Gray’s statistics, and more than 10,000 existed by the end of 1994.
Some notable websites established in 1994 include the websites for the White House, Microsoft, Pizza Hut, Yahoo, and sex.com. The first online transaction occurred in 1994 with the purchase of a large pepperoni and mushroom pizza with extra cheese from Pizza Hut. 1994 also happens to be the year that Jeff Bezos founded Amazon, formally registering the website in 1995.
Today, it is estimated that there are more than 3.91 billion websites in existence and more than 576,000 websites are created every day. Disruptive startups emerged to exploit the internet including Sun Microsystems, AOL, Netscape, MySpace, Yahoo, Google, AltaVista, Amazon, eBay, and Match.com.
NAVIGATING THE METAVERSE:
The metaverse may be a wild frontier, but here at NAB Amplify we’ve got you covered! Hand-selected from our archives, here are some of the essential insights you’ll need to expand your knowledge base and confidently explore the new horizons ahead:
- What Is the Metaverse and Why Should You Care?
- Avatar to Web3: An A-Z Compendium of the Metaverse
- The Metaverse is Coming To Get You. Is That a Bad Thing?
- Don’t Expect the Metaverse to Happen Overnight
- A Framework for the Metaverse from Hardware to Hollywood and Everything in Between
The power of creative destruction is exemplified by the fact that five of the world’s ten most valuable companies today exist solely due to the invention of the Internet: Amazon, Alphabet, Facebook, Tencent, and Alibaba.
Together with Apple and Microsoft, whose primary value relies on access to the Internet, these companies represent $10.2 Trillion in value. That is 76% of the value of the top ten and equivalent to 48% of the annual United States GDP. An argument can be made to include Tesla on this list, as it wholly relies on the Internet for its global sales engagement. Most importantly, those five companies (six, including Tesla) did not exist in 1993. Facebook is only 17 years old.
The emergence of the Metaverse to empower the Creator Economy will usher in another epochal change brought about through creative destruction.
The Metaverse will impact all our lives in unimaginable ways and bring about behavioral change. Industries will be completely transformed in less than a generation, societies will function significantly differently compared to today, businesses will operate in fundamentally different ways, and we will see the emergence of technologies and inventions that will exploit the fundamental behavioral changes that the Metaverse will enable.
Companies that are unknown to us today will emerge and dominate this new metaverse virtual economy and within a generation become the most valuable companies in the world. Creative destruction is assured.
The Mobile Internet
Fundamentally, the Internet from inception was a publishing platform and has been exceptionally good at written language (publication, storage, promotion, discovery, monetization, and search). It has never been particularly good at video, live communication, gaming, and social media. With the invention and introduction in 2007 of the iPhone, the Internet evolved into the mobile internet (often referred to as Internet 2.0). This took the Internet from being only accessible to users with costly personal computers and direct internet connections, to being accessible to anyone, anywhere who had a smartphone.
The mobile internet enabled websites to be accessible and interactive 24/7 using the tactile video display interface that mobile devices offered. This constant interactivity, along with the creation of device stores and the invention of apps, changed the way information and entertainment was produced and consumed. Real time interactivity is the fundamental power of the Internet 2.0 and the foundation of the Creator Economy. Importantly, we see the explosion since 2007 of gaming, social media, and User Generated Content (UGC) which seeds the impending emergence of the Metaverse.
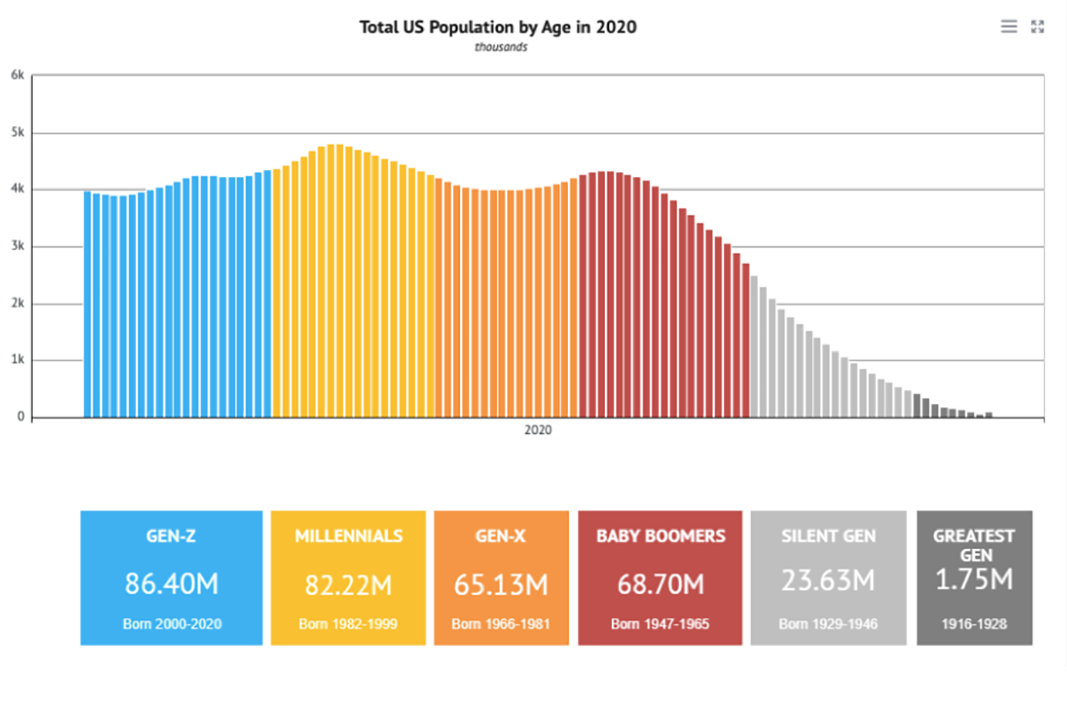
Companies including YouTube, Facebook, Snapchat, Twitter, Uber, Netflix, Airbnb, and many others emerge and dominate due to the unlimited access the mobile internet enabled. We have also seen the explosion in popularity and use of mobile accessible games, with 2.6 billion people playing mobile video games in 2020 and more than 80 billion downloads of mobile video games.
The United States is at an inflection point demographically in which 52% of its population is classified as Millennial (born 1982-1999) and Generation Z (born 2000-2020). These groups combined total 168 million people with an average age of 18 years old. These are the most sought-after consumers by the brand advertising industry, and they represent the first consumer generation conditioned to mobile device content consumption rather than television. These consumers spend more than 80% of their time on mobile devices in four categories: gaming, texting, social media, and entertainment and it is predominantly live. For these consumers, the four categories are inexorably linked, and the Metaverse provides the framework to combine them into a holistic, authentic, and immersive experience.
The Creator Economy is the reinvention of television in which control and monetization of content distribution is no longer dominated by a few large networks and media companies, but by the talent themselves who distribute directly to their audiences. It is the integration of content manufacturing and delivery with audience curation and discovery via social media and the mobile internet. It is dominated by User Generated Content (UGC) which is primarily edited videos made by individual creators and uploaded to streaming video on demand (SVOD) platforms like YouTube and Facebook.
More recently, User Generated Live Content (UGLC), which is harder and more costly to produce, has exploded via platforms like Twitch (owned by Amazon), YouTube Live, and Facebook Live. The scale of UGC networks dwarfs traditional media; popular YouTuber PewDiePie has 110 million YouTube subscribers and his videos have been viewed more than 27.5 billion times. Comcast, the largest cable TV subscription base, by comparison has 22 million subscribers.
Manuel Castells, in his essay “The Impact of the Internet on Society: A Global Perspective,” states that; ‘As in all moments of major technological change, people, companies, and institutions feel the depth of the change, but they are often overwhelmed by it, out of sheer ignorance of its effects”.
Therefore, it is Millennial and Generation Z consumers who grew up in the Creator Economy and are comfortable with the technology that enables the Metaverse that will accelerate the development and exploitation of the opportunities. Entrepreneurs will emerge from these generations who will creatively destroy business in nearly all industries. These entrepreneurs will be the next Bill Gates, Steve Jobs, and Jeff Bezos of the Metaverse economy, and one is already well known, Tim Sweeny – the founder of Epic Games.
The Metaverse
The Metaverse is the next generation of the Internet – the total convergence of streaming, interactivity, and social media. Content, communication, and interaction are presented spatially as deep, evocative experiences that drive consumer behavior and ultimately brand value. It is a virtual world where anyone can explore, experience, create, communicate, and participate in real time (think of Steven Spielberg’s film Ready Player One). The Metaverse will disrupt every sector of the economy and our daily lives, most notably; Retail, Entertainment and Leisure, Design, Manufacturing, Medicine, Education, Transport, Telecommunications, Travel, Social Media, User Interfaces, and Content Creation.
Some users will engage with it like they would a massive multiplayer video game, others will use it to interact with their smart devices, shop, and experience content. For industry, the Metaverse will support micron-accurate simulations of production processes and eliminate physical distance between teams.
The Metaverse will be the decisive technology of the Creator Economy, empowering the monetization and scale of live content and experiences by any UGLC creator in immersive, engaging, transactional social experiences with audiences. The Metaverse will be always on, always live, and enable real time experiences just like a city that never sleeps. Ultimately, it will become the dominant global platform for creating and watching live content with significant added features like interactivity, real time transactional functionality, branded promotion and integration, game mechanics and functionality, integrated socialization, blockchain and NFT capability, and deeply rewarding gamification tools.
“What the internet is for information, the metaverse is going to do for social connections. I’m no longer bound by physical distance or all these constraints in terms of who I interact with or how I represent who I am. All these things are suddenly unleased. It’s insanely disruptive.”
Roblox CEO Craig Donato
The primary entry point to the Metaverse will be via a browser-based URL and a personalized avatar that people will be able to use to navigate a virtual metaverse environment with a mobile device using typical game engine mechanics. Our endlessly customizable avatars will be virtual versions of ourselves that hold our keys, wallet, and identity. We will purchase digital assets for our avatars such as clothing and jewelry and we will determine how much, if any, of our data we allow branded metaverses to access for them to customize our experiences.
Ultimately there will be billions of metaverses and there are two primary types of metaverses:
- Closed metaverses and
- Open metaverses
A closed metaverse is only accessible through a download of a proprietary source IP which users are required to sign an end user license agreement to access. Video games like Fortnite, Roblox, Call of Duty, Minecraft, and League of Legends are all examples of closed metaverses.
Open metaverses are accessible by anyone who creates an avatar and enters it via a browser and a URL on a PC or mobile device. In the next few years, every brand in the world will need to invest in an open metaverse first strategy. Consider a global brand such as the Ford Motor Company. Today anyone can access the Ford website via a browser and find hundreds of pages of content created by Ford about their current range of cars available for sale, and a myriad of pages about options, finance, and service. It is a one-dimensional experience focused on reading. I cannot talk to other potential Ford customers or a Ford salesperson like I can if I walk into a dealership, I cannot get into a car, and I can’t drive a virtual model of a car. A Ford metaverse would enable all that and much more for my personalized avatar. I could learn about Ford’s history, its importance in the early development of automotive technology, I could experience a virtual Ford museum tour and get up close and personal with every car ever made by Ford in its history, I could experience driving a Ford GT on a race track, possibly with a Ford sponsored race car driver, I could purchase customized Ford merchandise and memorabilia both real and digital, and I can transact the purchase of a car. The metaverse experience for consumers will be infinitely immersive and authentic and for both brands and consumers, deeply enriching.

The metaverse enables real time interactions that Internet 2.0 cannot. On Ford’s current website, unless I create an account and sign into it, Ford does not gather any granular data about me and my reason for landing on their webpage. They may collect my IP address and know what pages I clicked on and how long I spent there, but in the metaverse I can choose how much data l let Ford know. If I am in the market for a new car and want to engage with Ford, I could let them know my name and certain demographical information. My avatar could engage in real time with a salesperson, take a test drive of the cars I am considering, or bring a friend or family member into the Ford metaverse to browse with me. This immersive, interactive engagement has long been the holy grail of the brand marketplace and the Metaverse delivers it.
The Metaverse also excels in the augmentation, advancement, and enrichment of real time social media interactions. The Metaverse enables interaction in a way that replicates the physical way we communicate with the addition of AI tools. In the future, our avatars will meet friends in a metaverse to explore and share common experiences, go shopping together, visit family and friends, attend virtual concerts and conventions, visit galleries and museums, even go to school. We will share our virtual experiences on our other social media platforms #livefromthemetaverse and some of us will live stream our metaverse experiences and interactions for passive consumption by our followers on platforms such as Twitch. The Metaverse will power communities in unique ways. Certain communities that scale will create their own metaverses and operate their own economies. The breadth of opportunity that the metaverse empowers is enormous.
The Metaverse is already here. Some of the world’s largest companies are heavily investing in their version of the metaverse alongside the nimble startups who are pioneering the future of the Metaverse.
For me, it is 1993 all over again. The difference this time is that I am ready to help build the Metaverse with Infinite Reality. Creative Destruction is assured.




Discussion
Responses (3)